Research: Atomic Force Microscopy, Past Studies
Topic: Nucleosome
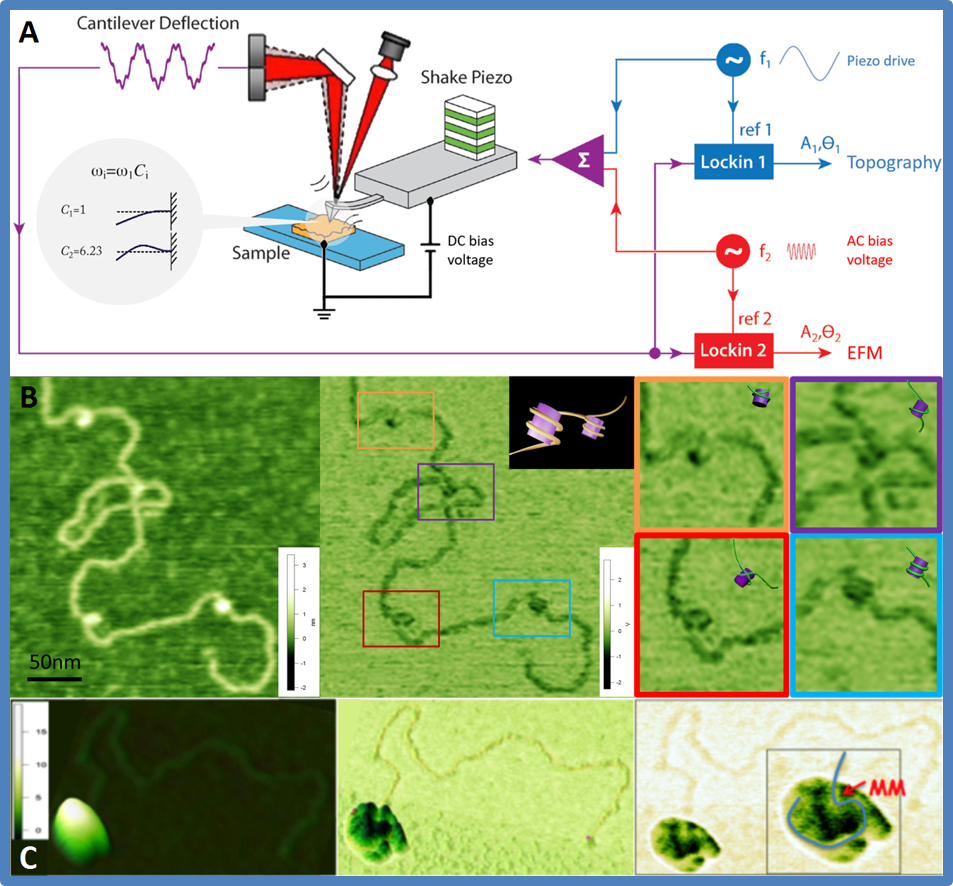
Dual Resonance Frequency Enhanced Electrostatic Microscopy (DREEM) is a variant of electrostatic force microscopy (EFM), which is an AFM based technique. A schematic illustration of the technique and sample images are shown below.
Figure. DREEM IMAGING
- DREEM basics: Based on electrostatic force microscopy (EFM), DREEM utilizes the multi-frequency resonance nature of AFM cantilevers by simultaneously applying an piezo driven oscillation at the fundamental frequency and an AC bias voltage at the first over tone. Topographic images and electrostatic images are generated simultaneously by monitoring the fundamental frequency and first overtone respectively at the same time.
- DREEM imaging of a nucleosome complex. Topography (left), DREEM phase (middle), and zoomed in areas (right) of DREEM phase are shown. Modeling of DNA around the histones based on DREEM phase and crystal structures are displayed in the insets. The DREEM image reveals dynamic ways DNA could wrap around the histones.
- Topography (left) and DREEM phase (middle & right) images of a large MutSα-MutLα-DNA complex containing ~10 proteins. In the AFM image of the complex, the DNA measures ~120 nm too short. The DREEM image reveals that this missing DNA is wrapped in the complex (the path of the DNA is traced in the inset). Interestingly, the DNA appears to be sharply bent after entering the complex at the expected position of the mismatch (MM).
Read more in the published article.